Chlorine azide
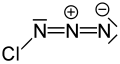 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Chlorine azide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
| ||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
PubChem CID |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
| ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula | ClN3 | ||
| Molar mass | 77.4731 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Yellow-orange liquid; colorless gas | ||
| Melting point | −100 °C (−148 °F; 173 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −15 °C (5 °F; 258 K) | ||
| Solubility | Soluble[vague] in butane, pentane, benzene, methanol, ethanol, diethyl ether, acetone, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and carbon disulfide; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Structure | |||
| orthorhombic | |||
| Cmc 21, No. 36[1] | |||
| Explosive data | |||
| Shock sensitivity | Extreme | ||
| Friction sensitivity | Extreme | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards | Extremely sensitive explosive | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |  0 4 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds | Hydrazoic acid Fluorine azide Bromine azide Iodine azide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |||
Chlorine azide (ClN3) is an inorganic compound that was discovered in 1908 by Friedrich Raschig.[2] Concentrated ClN3 is notoriously unstable and may spontaneously detonate at any temperature.[3]
Preparation and handling
Chlorine azide is prepared by passing chlorine gas over silver azide, or by an addition of acetic acid to a solution of sodium hypochlorite and sodium azide.[4]
Explosive characteristics
Chlorine azide is extremely sensitive. It may explode, sometimes even without apparent provocation; it is thus too sensitive to be used commercially unless first diluted in solution. Chlorine azide reacts explosively with 1,3-butadiene, ethane, ethene, methane, propane, phosphorus, silver azide, and sodium. On contact with acid, chlorine azide decomposes, evolving toxic and corrosive hydrogen chloride gas.[5]
Regulatory information
Its shipment is subject to strict reporting requirements and regulations by the US Department of Transportation.
References
- ^ Lyhs, Benjamin; Bläser, Dieter; Wölper, Christoph; Schulz, Stephan; Jansen, Georg (2012). "A Comparison of the Solid‐State Structures of Halogen Azides XN3 (X=Cl, Br, I)". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 51 (51): 12859–12863. doi:10.1002/anie.201206028. PMID 23143850.
- ^ Frierson, W. J.; Browne, A. W. (1943). "Chlorine Azide. II. Interaction of Chlorine Azide and Silver Azide. Azino Silver Chloride, N3AgCl". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 65 (9): 1698–1700. doi:10.1021/ja01249a013.
- ^ Frierson, W. J.; Kronrad, J.; Browne, A. W. (1943). "Chlorine Azide, ClN3. I.". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 65 (9): 1696–1698. doi:10.1021/ja01249a012.
- ^ Raschig, F. (1908). "Über Chlorazid N3Cl". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 41 (3): 4194–4195. doi:10.1002/cber.190804103130.
- ^ CID 61708 from PubChem
External links
 Media related to Chlorine azide at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chlorine azide at Wikimedia Commons
- v
- t
- e
- ClF
- ClF3
- ClF5
- ClO
- ClO2
- Cl2O
- Cl2O2
- Cl2O3
- Cl2O4
- Cl2O5
- Cl2O6
- Cl2O7
- ClO4
- ClOF
- ClOF3
- ClO2F
- ClOF5 (predicted)
- ClO2F3
- ClO3F
- ClNO3
- ClSO3F
- ClN3
- Cl3N














